Advertisement
Debt consolidation home equity loans offer a potential solution for individuals seeking to simplify their debt obligations and potentially lower their monthly payments. By leveraging the equity built up in your home, you can consolidate multiple debts into a single loan with a potentially lower interest rate. However, this strategy comes with inherent risks, including the possibility of losing your home if you fail to repay the loan. Understanding the intricacies of debt consolidation home equity loans is crucial before making a decision, as it requires careful consideration of your financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term goals.
This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of debt consolidation home equity loans, exploring their advantages and disadvantages, eligibility criteria, costs, and potential risks. We’ll also examine alternative debt consolidation options and provide insights into finding the right lender for your needs. By understanding the complexities of this financial tool, you can make an informed decision about whether a debt consolidation home equity loan is the right path for your unique circumstances.
What is a Debt Consolidation Home Equity Loan?
 home equity loan” title=”” />
home equity loan” title=”” />
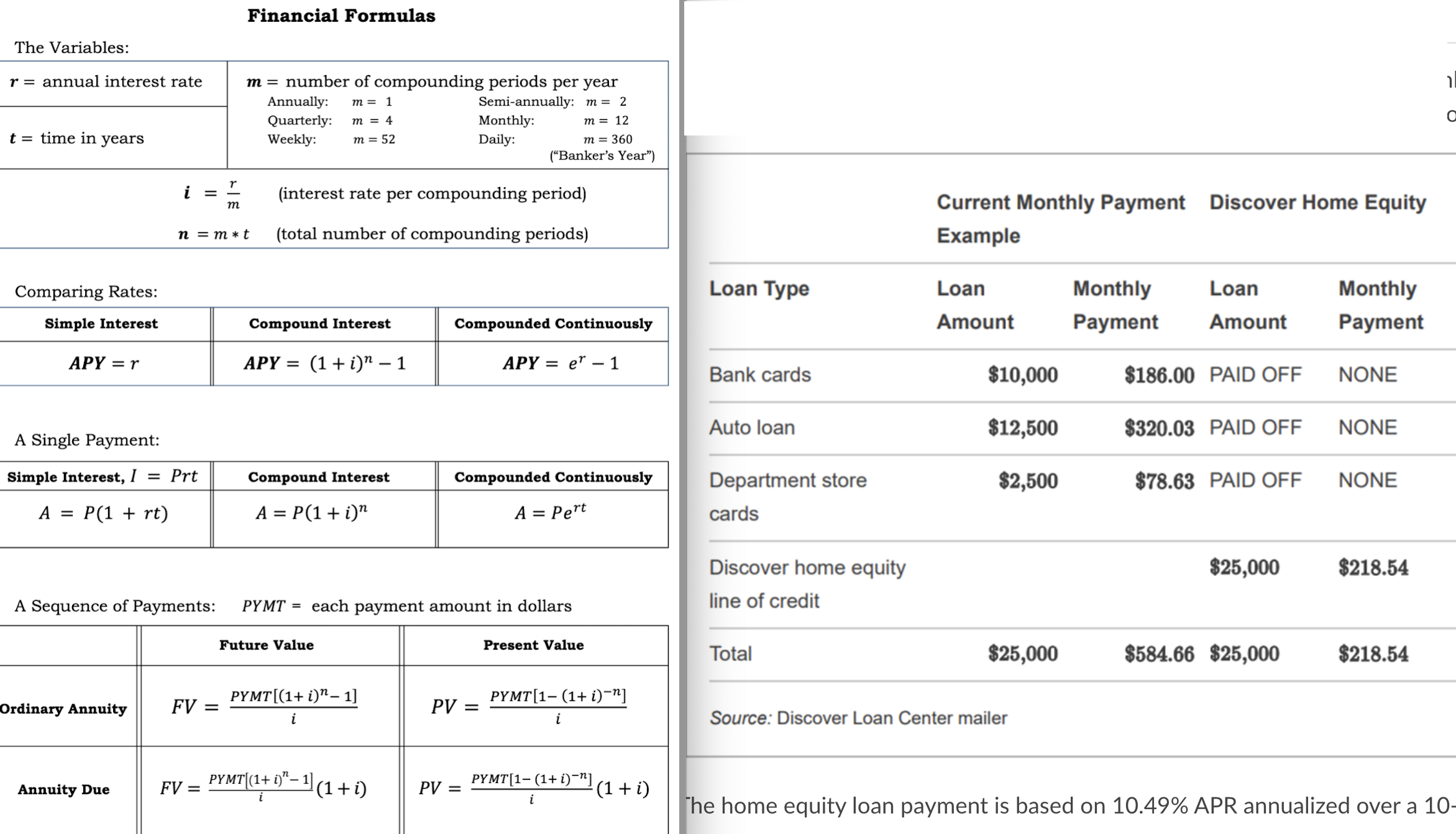
A debt consolidation home equity loan is a type of loan that allows homeowners to borrow against the equity they have built up in their homes to pay off other debts. This can be a useful tool for consolidating high-interest debt, such as credit cards or personal loans, into a single, lower-interest loan.
How a Debt Consolidation Home Equity Loan Works
A home equity loan is a second mortgage that is secured by your home. This means that the lender has the right to foreclose on your home if you fail to make your payments. The amount of money you can borrow is based on the equity you have in your home, which is the difference between the current market value of your home and the amount you still owe on your mortgage.
For example, if your home is worth $300,000 and you owe $150,000 on your mortgage, you have $150,000 in equity. You could potentially borrow up to $150,000 with a home equity loan.
Advantages of Using a Home Equity Loan for Debt Consolidation
- Lower Interest Rates: Home equity loans typically have lower interest rates than credit cards or personal loans. This can save you money on interest payments over time.
- Fixed Monthly Payments: Home equity loans typically have fixed monthly payments, which can help you budget and plan for your finances.
- Simplified Debt Management: Consolidating your debt into a single loan can simplify your debt management. You will only have one payment to make each month, rather than multiple payments to different lenders.
Disadvantages of Using a Home Equity Loan for Debt Consolidation
- Risk of foreclosure: If you fail to make your payments on a home equity loan, the lender can foreclose on your home. This is a serious risk that you should carefully consider before taking out a home equity loan.
- High Interest Rates Compared to Other Options: While home equity loans typically have lower interest rates than credit cards or personal loans, they may have higher interest rates than other debt consolidation options, such as a personal loan or balance transfer credit card.
- Loss of Equity: Borrowing against your home equity reduces the amount of equity you have in your home. This can make it more difficult to refinance your mortgage or sell your home in the future.
How Does Debt Consolidation Work?
debt consolidation is a strategy that involves combining multiple debts into a single loan with a new interest rate and payment schedule. A home equity loan can be used to consolidate various debts, such as credit cards, personal loans, and medical bills.
By consolidating your debt, you may be able to simplify your finances and potentially save money on interest. However, it’s important to carefully consider the risks and benefits before taking out a home equity loan for debt consolidation.
Steps Involved in Applying for a Home Equity Loan for Debt Consolidation, Debt consolidation home equity loan
Applying for a home equity loan for debt consolidation involves a series of steps, similar to obtaining any other loan. It’s crucial to understand these steps and gather the necessary documentation before initiating the application process.
- Determine your home equity: The first step is to calculate how much equity you have in your home. This is the difference between your home’s current market value and the outstanding balance on your mortgage. Lenders typically require a minimum amount of equity, usually 15% to 20%, for a home equity loan.
- Shop around for lenders: Once you know your home equity, you can start comparing offers from different lenders. It’s essential to consider factors such as interest rates, loan terms, and fees. You can use online comparison tools or contact lenders directly to gather information.
- Gather required documents: Lenders will require various documents to process your application. These typically include proof of income, recent pay stubs, tax returns, and your home’s appraisal. It’s helpful to gather all necessary documents before submitting your application.
- Submit your application: After gathering all the required documents, you can submit your application. This may involve filling out an online form, visiting a lender’s office, or contacting a loan officer.
- Loan approval and closing: Once your application is approved, you will receive a loan agreement outlining the terms and conditions of your home equity loan. You will then need to sign the loan agreement and complete the closing process. This typically involves meeting with a lender representative to finalize the loan and receive the funds.
Factors Lenders Consider When Approving a Home Equity Loan for Debt Consolidation
Lenders assess various factors when deciding whether to approve a home equity loan for debt consolidation. These factors play a crucial role in determining your eligibility and the loan terms you receive.
- credit score: Your credit score is a key indicator of your creditworthiness. Lenders generally prefer borrowers with higher credit scores, as it suggests a lower risk of default. A good credit score can qualify you for better interest rates and loan terms.
- Debt-to-income ratio: This ratio measures your monthly debt payments against your gross monthly income. Lenders prefer borrowers with lower debt-to-income ratios, indicating a greater ability to manage their debt obligations. A high debt-to-income ratio may make it more difficult to obtain a loan or result in less favorable terms.
- Home equity: As mentioned earlier, lenders require a minimum amount of equity in your home to secure the loan. This ensures they have sufficient collateral in case of default. A higher equity position generally translates to more favorable loan terms.
- Income and employment history: Lenders assess your income and employment history to determine your ability to repay the loan. A stable income and a consistent employment history demonstrate financial stability and increase your chances of loan approval.
- Loan-to-value ratio (LTV): This ratio represents the amount of the loan compared to the value of your home. Lenders generally have limits on the LTV for home equity loans. A lower LTV, indicating a smaller loan amount relative to your home’s value, may result in better interest rates and terms.
Costs and Risks Associated with Debt Consolidation Home Equity Loans

Debt consolidation home equity loans can seem like a good way to simplify your finances and save money on interest. However, it’s essential to understand the associated costs and risks before making a decision. This section will provide a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with a home equity loan and discuss the potential risks involved in using a home equity loan for debt consolidation.
Costs Associated with Home Equity Loans
The costs associated with a home equity loan can vary depending on the lender, the loan amount, and the borrower’s creditworthiness. However, some common costs include:
- Origination fees: These fees are charged by the lender to cover the administrative costs of processing the loan. Origination fees are typically a percentage of the loan amount, ranging from 1% to 3%. For example, a $50,000 home equity loan with a 2% origination fee would cost you $1,000.
- Closing costs: These fees cover various expenses related to the closing of the loan, such as appraisal fees, title insurance, and recording fees. Closing costs can range from 2% to 5% of the loan amount.
- Interest rates: Home equity loans typically have variable interest rates, which means the rate can fluctuate over time. This can make it difficult to budget for your monthly payments, as the amount you owe can increase if interest rates rise. Variable rates are generally higher than fixed rates, but they can be lower if you have a good credit score.
- Property taxes and homeowners insurance: You’ll need to continue paying your property taxes and homeowners insurance, even if you use your home equity loan to consolidate your debt. These costs can add up over time.
Risks Associated with Home Equity Loans
While home equity loans can offer a lower interest rate than other types of debt, they also come with several risks:
- Risk of foreclosure: If you default on your home equity loan payments, the lender can foreclose on your home. This means you could lose your home and any equity you have built up in it.
- Risk of negative equity: If your home’s value decreases, you could end up with negative equity, which means you owe more on your mortgage than your home is worth. This can make it difficult to sell your home or refinance your mortgage.
- Risk of high interest rates: Home equity loans typically have variable interest rates, which means the rate can fluctuate over time. This can make it difficult to budget for your monthly payments, as the amount you owe can increase if interest rates rise.
Comparison of Interest Rates
home equity loans typically have lower interest rates than credit cards and personal loans. However, they are often higher than other debt consolidation options, such as balance transfers. Here is a comparison of interest rates for different debt consolidation options:
| Debt Consolidation Option | Typical Interest Rate |
|---|---|
| Home Equity Loan | 4% to 8% |
| Personal Loan | 6% to 14% |
| Balance Transfer Credit Card | 0% to 20% |
It’s important to note that these interest rates are just averages and can vary depending on your credit score, the lender, and the loan amount.
Alternatives to Debt Consolidation Home Equity Loans
While a home equity loan can be a viable option for debt consolidation, it’s crucial to explore other alternatives before committing to this route. Each method has its own pros and cons, and the best choice for you will depend on your individual financial circumstances.
Debt Management Plans
Debt management plans, offered by non-profit credit counseling agencies, help you consolidate your debts into a single monthly payment with a lower interest rate.
Pros:
- Lower interest rates: Credit counseling agencies negotiate with creditors to lower interest rates and monthly payments.
- Reduced monthly payments: A single, lower monthly payment can make it easier to manage your debt.
- No upfront fees: Most credit counseling agencies offer free consultations and do not charge upfront fees.
Cons:
- Limited debt types: Not all debts are eligible for debt management plans, and some creditors may not participate.
- Credit score impact: Your credit score may be negatively affected during the debt management plan period, as accounts are often reported as “paid as agreed” instead of “paid in full.”
- Lengthy process: It can take several years to complete a debt management plan.
Balance Transfers
Balance transfers involve transferring your existing debt to a new credit card with a lower interest rate. This can save you money on interest charges and help you pay off your debt faster.
Pros:
- Lower interest rates: Credit cards with 0% introductory APRs can help you save on interest for a set period.
- Convenience: A single credit card simplifies debt management and makes tracking payments easier.
Cons:
- Limited time: Introductory APRs typically last for a limited period, after which a higher interest rate may apply.
- Balance transfer fees: Most credit cards charge a balance transfer fee, which can be a percentage of the transferred amount.
- Credit score impact: Applying for a new credit card can temporarily lower your credit score.
Debt Settlement
Debt settlement involves negotiating with creditors to settle your debts for less than the full amount owed. This can be a viable option if you’re struggling to make payments and want to reduce your debt burden.
Pros:
- Lower debt amount: You can significantly reduce your debt by settling for a lower amount.
- Faster debt payoff: Settling your debts can help you pay them off faster than traditional repayment methods.
Cons:
- Credit score impact: Debt settlement can severely damage your credit score, as it’s reported as a “charged-off” account.
- Legal consequences: Some creditors may pursue legal action if you fail to settle your debts as agreed.
- Fees: Debt settlement companies often charge high fees, which can reduce the savings you realize.
Personal Loans
Personal loans offer a fixed interest rate and a set repayment term, making them a predictable way to consolidate debt.
Pros:
- Fixed interest rate: You’ll know exactly how much interest you’ll pay over the life of the loan.
- Set repayment term: You’ll have a clear timeline for paying off your debt.
- Potential for lower interest rates: Personal loans can offer lower interest rates than credit cards, especially if you have good credit.
Cons:
- Credit score impact: Applying for a personal loan can temporarily lower your credit score.
- Loan approval: You may not qualify for a personal loan if you have poor credit or a high debt-to-income ratio.
When a Debt Consolidation Home Equity Loan Might Be Right for You
A debt consolidation home equity loan can be a valuable tool for managing your finances, but it’s crucial to carefully consider your situation before taking this step. This type of loan can be advantageous in certain circumstances, offering the potential to simplify your debt management and potentially save money on interest.
Situations Where a Home Equity Loan Might Be Beneficial
Here are some scenarios where a debt consolidation home equity loan could be a viable option:
| Situation | Benefits |
|---|---|
| You have high-interest debt, such as credit cards or personal loans. | By consolidating your debt into a home equity loan with a lower interest rate, you can potentially save money on interest payments and reduce your overall debt burden. |
| You have a substantial amount of equity in your home. | A home equity loan allows you to borrow against the equity you’ve built in your home, providing access to a larger loan amount. |
| You have a good credit score. | A strong credit score increases your chances of qualifying for a home equity loan with favorable terms, such as a lower interest rate. |
| You have a stable income and a solid repayment plan. | Lenders typically prefer borrowers with a reliable income stream and a well-defined plan for repaying the loan. |
Factors to Consider Before Using a Home Equity Loan for Debt Consolidation
While a home equity loan might seem appealing, it’s crucial to weigh the potential benefits against the risks before making a decision. Here are some important factors to consider:
- Interest rates: While home equity loans often have lower interest rates than credit cards, they may still be higher than other types of loans. Compare interest rates from different lenders before deciding.
- Loan terms: Consider the loan term and how long it will take to repay the loan. A longer term might mean lower monthly payments but also higher overall interest costs.
- Closing costs: Home equity loans typically involve closing costs, which can add to the overall cost of the loan. Ensure you factor these costs into your calculations.
- Risk of foreclosure: If you default on your home equity loan, you could risk losing your home. It’s essential to have a solid repayment plan and ensure you can comfortably afford the monthly payments.
- Impact on your credit score: Taking out a home equity loan can affect your credit score, especially if you already have a high debt-to-income ratio. Monitor your credit score closely after obtaining the loan.
Questions to Ask Yourself Before Applying for a Home Equity Loan
Before applying for a home equity loan, it’s essential to thoroughly assess your financial situation and determine if this loan is the right choice for you. Consider these questions:
- Do I have a clear understanding of my current debt situation and my ability to repay a home equity loan?
- Have I explored other debt consolidation options, such as balance transfers or debt management programs?
- Am I comfortable with the potential risks associated with a home equity loan, such as the possibility of foreclosure?
- Do I have a solid plan in place to avoid accumulating new debt after consolidating my existing debt?
- Have I compared interest rates and loan terms from multiple lenders to ensure I’m getting the best deal?
