refinance home loan debt consolidation presents a compelling strategy for homeowners seeking to simplify their financial landscape and potentially reduce their overall debt burden. This approach leverages the equity built in your home to consolidate high-interest debts into a single, lower-interest loan, potentially leading to significant savings over time. By understanding the nuances of refinancing and its potential benefits and drawbacks, homeowners can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Refinancing for debt consolidation can be a powerful tool, but it's not without its complexities. Carefully considering factors such as current interest rates, debt-to-income ratio, and long-term financial objectives is crucial before embarking on this path. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of refinancing for debt consolidation, empowering you to navigate this process with confidence.
Understanding Home Loan Refinancing
 debt consolidation" title="Loan amortization schedule spreadsheet excel template use" />
Refinancing your home loan is a process where you replace your existing mortgage with a new one, typically with different terms and conditions. This can be a valuable tool for homeowners seeking to lower their monthly payments, reduce their interest rate, or access cash from their home equity.
debt consolidation" title="Loan amortization schedule spreadsheet excel template use" />
Refinancing your home loan is a process where you replace your existing mortgage with a new one, typically with different terms and conditions. This can be a valuable tool for homeowners seeking to lower their monthly payments, reduce their interest rate, or access cash from their home equity.
Types of Refinancing Options
Refinancing options vary depending on your financial goals and circumstances. The most common types include:- Rate-and-Term Refinancing: This is the most basic type of refinance, where you simply replace your existing mortgage with a new one at a lower interest rate. The loan term can be adjusted, but the principal amount remains the same. For example, you could refinance a 30-year mortgage to a 15-year mortgage at a lower interest rate, resulting in faster repayment and lower overall interest costs.
- Cash-Out Refinancing: This option allows you to borrow more than your existing mortgage balance, allowing you to access cash from your home equity. This can be used for various purposes, such as home improvements, debt consolidation, or even funding college tuition. However, it's important to note that cash-out refinancing increases your loan balance and potentially your monthly payments.
Potential Benefits of Refinancing
Refinancing can offer several advantages, including:- Lower Interest Rates: Refinancing to a lower interest rate can significantly reduce your monthly payments and save you money over the life of your loan. For example, refinancing a $200,000 mortgage with a 5% interest rate to a 3% interest rate can save you thousands of dollars in interest payments over the loan term.
- Reduced Monthly Payments: Lower interest rates can lead to lower monthly payments, freeing up cash flow for other financial goals or simply providing more financial flexibility. This can be particularly beneficial if you're struggling to make your current mortgage payments.
- Access to Cash: Cash-out refinancing allows you to tap into your home equity, providing access to funds for various purposes. This can be a valuable option for homeowners who need to make significant home improvements, consolidate debt, or cover unexpected expenses.
Potential Drawbacks of Refinancing
While refinancing can offer numerous benefits, it's essential to consider the potential drawbacks:- Closing Costs: Refinancing involves closing costs, which can include origination fees, appraisal fees, and title insurance. These costs can vary depending on the lender and the loan amount, but they can add up significantly.
- Origination Fees: Lenders typically charge an origination fee, which is a percentage of the loan amount. This fee helps cover the lender's administrative costs associated with processing the refinance loan.
- Potential Penalties: Some mortgages have prepayment penalties, which can be incurred if you refinance your loan before a specific period. It's crucial to review your existing mortgage documents to understand any potential penalties associated with refinancing.
Debt Consolidation Through Refinancing: Refinance Home Loan Debt Consolidation
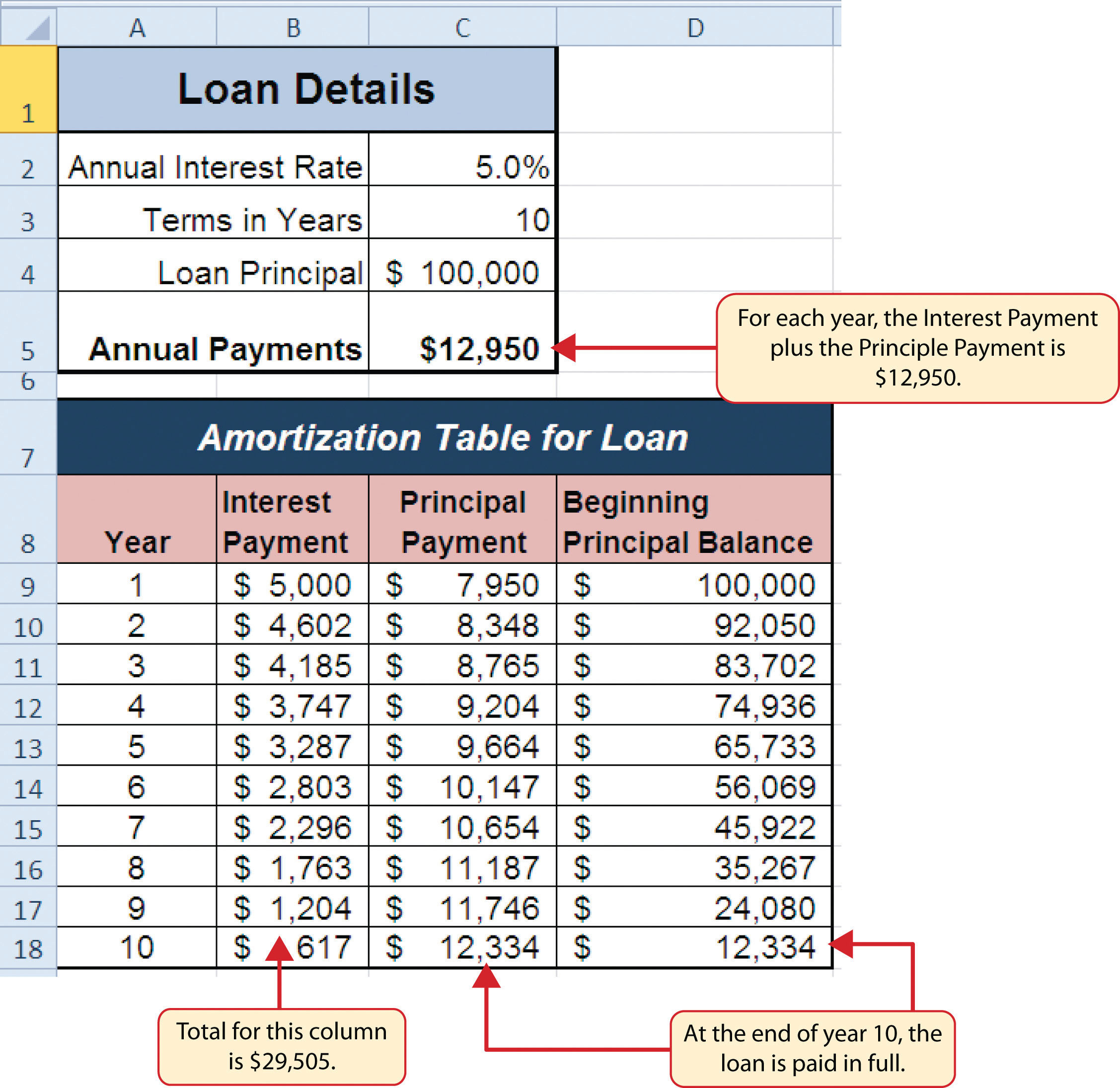 Refinancing your home loan can be a powerful tool for consolidating high-interest debt, allowing you to streamline your finances and potentially save money. By leveraging the equity in your home, you can access a lower interest rate loan to pay off other debts, such as credit cards, personal loans, or medical bills. This strategy can help you reduce your overall monthly payments, shorten the repayment period, and potentially improve your credit score.
Refinancing your home loan can be a powerful tool for consolidating high-interest debt, allowing you to streamline your finances and potentially save money. By leveraging the equity in your home, you can access a lower interest rate loan to pay off other debts, such as credit cards, personal loans, or medical bills. This strategy can help you reduce your overall monthly payments, shorten the repayment period, and potentially improve your credit score.
Benefits of Debt Consolidation Through Refinancing
Debt consolidation through refinancing offers several advantages:- Simplifying Payments: Instead of managing multiple loan payments with varying interest rates and due dates, you consolidate them into a single, manageable monthly payment. This simplifies your budgeting and reduces the risk of missing payments.
- Reducing Interest Rates: By refinancing your home loan, you can potentially secure a lower interest rate than your existing debts, especially if you have high-interest credit card debt. This can significantly reduce your overall interest charges and save you money over time.
- Improving Credit Scores: Successfully consolidating debt through refinancing can positively impact your credit score. By reducing your credit utilization ratio (the amount of credit you're using compared to your total available credit) and making timely payments, you can demonstrate responsible financial behavior to credit bureaus.
Comparing Home Equity Loans and Cash-Out Refinances
When considering debt consolidation through refinancing, you have two primary options: a home equity loan or a cash-out refinance.- Home Equity Loans: A home equity loan is a second mortgage that allows you to borrow against the equity you've built in your home. This loan is typically secured by your property and comes with a fixed interest rate. Home equity loans are often used for debt consolidation, home improvements, or other major expenses.
- Cash-Out Refinances: A cash-out refinance involves refinancing your existing mortgage for a larger amount than your current loan balance. The difference between the new loan amount and the outstanding balance is paid out to you in cash. You can use this cash to pay off other debts, but it increases your overall mortgage balance and extends your repayment term.
| Feature | Home Equity Loan | Cash-Out Refinance |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Type | Second Mortgage | Mortgage Refinancing |
| Interest Rate | Fixed | Fixed or Adjustable |
| Loan Term | Typically 5-15 years | Typically 15-30 years |
| Loan Amount | Limited by your home equity | Up to the appraised value of your home |
| Closing Costs | Lower than a refinance | Higher than a home equity loan |
| Impact on Credit Score | May have a slight negative impact | Can have a significant impact, both positive and negative |
Debt Consolidation Methods Comparison
To make an informed decision, it's crucial to compare refinancing with other debt consolidation methods:- Personal Loans: Personal loans offer a fixed interest rate and a fixed repayment term. They are unsecured loans, meaning they don't require collateral. However, interest rates can be higher than refinancing options.
- Balance Transfers: Credit card balance transfers allow you to move your existing credit card balances to a new card with a lower interest rate. This can help you save on interest charges but may involve balance transfer fees.
The Refinancing Process
 Refinancing your home loan for debt consolidation involves replacing your existing mortgage with a new one, often with more favorable terms, to pay off other debts. This process can streamline your finances, lower your monthly payments, and potentially save you money on interest.
Refinancing your home loan for debt consolidation involves replacing your existing mortgage with a new one, often with more favorable terms, to pay off other debts. This process can streamline your finances, lower your monthly payments, and potentially save you money on interest.
Steps Involved in Refinancing
The refinancing process involves several steps:- Assess Your Financial Situation: Begin by reviewing your current debt obligations, interest rates, and credit score. Determine how much debt you wish to consolidate and the potential savings you could achieve through refinancing.
- Shop Around for Lenders: Compare rates and terms from multiple lenders, including banks, credit unions, and online mortgage providers. Consider factors like loan fees, closing costs, and interest rate lock periods.
- Get Pre-Approved for a Loan: Once you've identified a lender with attractive terms, get pre-approved for a loan. This demonstrates your financial readiness and provides an estimated loan amount.
- Gather Necessary Documentation: Prepare documents such as your most recent pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements, and proof of homeownership. Lenders will need these to verify your financial information.
- Submit Your Application: Complete and submit your loan application, including all required documentation. Lenders will review your application and assess your creditworthiness.
- Home Appraisal: The lender will order a home appraisal to determine the current market value of your property. This ensures the loan amount doesn't exceed the property's value.
- Loan Approval and Closing: If your application is approved, you'll receive a loan commitment letter outlining the final loan terms. You'll then schedule a closing meeting to finalize the loan and receive the funds to pay off your existing debts.
Finding the Best Refinancing Rates and Terms, Refinance home loan debt consolidation
To secure the best refinancing rates and terms, follow these tips:- Improve Your credit score: A higher credit score often translates to lower interest rates. Before applying for a refinance, take steps to improve your credit score, such as paying bills on time and reducing credit card debt.
- Shop Around for Lenders: Compare rates and terms from multiple lenders to find the most competitive offers. Consider using online mortgage calculators and comparing interest rates from different institutions.
- Negotiate with Lenders: Don't hesitate to negotiate with lenders to secure favorable terms. Discuss potential concessions like lower interest rates, reduced closing costs, or a shorter loan term.
- Consider Loan Types: Explore different loan types, such as fixed-rate or adjustable-rate mortgages, to determine which best suits your financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Understand Loan Fees: Be aware of various loan fees, such as origination fees, appraisal fees, and closing costs. Factor these fees into your overall loan cost and compare them across lenders.
Documentation Required for Refinancing
Lenders typically require the following documentation during the refinancing process:- Proof of Income: Pay stubs, tax returns, and W-2 forms are used to verify your income and debt-to-income ratio.
- Bank Statements: Recent bank statements are needed to demonstrate your cash flow and financial stability.
- Credit Report: A credit report provides a detailed history of your credit usage and payment history, which is crucial for assessing your creditworthiness.
- Homeownership Documentation: Documents such as your mortgage statement, deed, and property tax records confirm your ownership of the property.
- Other Documents: Depending on the specific lender and loan program, you may need additional documents, such as a home appraisal, insurance policy, or a copy of your driver's license.
Negotiating with Lenders for Favorable Terms
Negotiating with lenders is essential to secure favorable refinancing terms:- Research Current Market Rates: Before negotiating, research current mortgage rates and compare them to the lender's offer. This gives you a benchmark for a fair deal.
- Highlight Your Strengths: Emphasize your strong credit score, low debt-to-income ratio, and history of on-time payments. This demonstrates your financial responsibility and increases your leverage.
- Be Prepared to Walk Away: If you're not satisfied with the lender's offer, be prepared to walk away and explore other options. This shows you're serious about finding the best deal.
- Consider Loan Bundles: Inquire about potential discounts or incentives if you bundle your mortgage with other financial products, such as checking accounts or credit cards, offered by the lender.
- Negotiate Closing Costs: Explore options for reducing closing costs, such as asking the lender to pay certain fees or seeking a lower interest rate in exchange for higher closing costs.
Considerations for Debt Consolidation Through Refinancing
 Refinancing your home loan to consolidate debt can be a smart financial move, but it's crucial to understand the potential risks and implications before making a decision. This section will delve into some key considerations that can help you determine if debt consolidation through refinancing is the right choice for you.
Refinancing your home loan to consolidate debt can be a smart financial move, but it's crucial to understand the potential risks and implications before making a decision. This section will delve into some key considerations that can help you determine if debt consolidation through refinancing is the right choice for you.
Risks Associated with Using Home Equity for Debt Consolidation
Using your home equity to consolidate debt comes with inherent risks. Your home is your most valuable asset, and leveraging it for debt consolidation could put you at risk if you're unable to repay the loan.- Increased Risk of foreclosure: If you fail to make your mortgage payments, you could face foreclosure, losing your home.
- Higher Monthly Payments: A larger loan amount may result in higher monthly payments, making it more challenging to manage your finances.
- Loss of Equity: If your home value declines, you might end up with less equity than you initially had, potentially making it difficult to refinance or sell your home in the future.
Importance of Maintaining a Strong Credit Score During the Refinancing Process
A strong credit score is essential when refinancing your home loan. Lenders use your credit score to assess your creditworthiness and determine the interest rate they'll offer. A higher credit score generally translates to a lower interest rate, which can save you money in the long run.- Impact on Interest Rates: A higher credit score often leads to lower interest rates, reducing your monthly payments and overall borrowing costs.
- Increased Approval Chances: Lenders are more likely to approve your refinancing application if you have a good credit history.
- Improved Loan Terms: A strong credit score may also make you eligible for better loan terms, such as a longer repayment period or a lower down payment.
Potential Tax Implications of Refinancing
Refinancing your home loan can have tax implications. It's crucial to understand these implications before proceeding.- Interest Deductibility: mortgage interest is typically deductible on federal income taxes, but the rules can be complex. Consult a tax professional to determine your specific deductibility.
- Loan Origination Fees: Loan origination fees, often charged by lenders, may be deductible as points on your mortgage.
- Penalty for Early Repayment: Some loans may have a prepayment penalty if you refinance before a specific period.
Resources and Tools for Consumers Seeking to Refinance Their Home Loans
Several resources and tools can assist consumers seeking to refinance their home loans.- Credit Reporting Agencies: Check your credit reports from the three major credit reporting agencies (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) to ensure accuracy and identify any errors that could impact your credit score.
- Online Mortgage Calculators: Use online mortgage calculators to estimate your monthly payments and compare different loan options.
- Financial Advisors: Consult a financial advisor to discuss your financial situation and explore refinancing options.
- Consumer Protection Agencies: Contact consumer protection agencies like the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) for information and assistance with mortgage-related issues.
