Home owners loan calculator is a powerful tool that can help you navigate the complex world of home financing. Whether you're looking to purchase a new home, refinance your existing mortgage, or fund home improvements, understanding the different loan options and their associated costs is crucial. By utilizing a homeowner loan calculator, you can gain valuable insights into the financial implications of your decisions, empowering you to make informed choices that align with your financial goals.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of homeowner loan calculators, exploring their functionality, benefits, and potential pitfalls. We will also discuss key factors to consider when choosing a loan, including interest rates, loan terms, and lender reputation. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of how to effectively utilize a homeowner loan calculator to make sound financial decisions regarding your home ownership journey.
Understanding Homeowner Loans
Mortgages
Mortgages are the most common type of homeowner loan. They are used to finance the purchase of a home, with the property serving as collateral for the loan.- Fixed-Rate Mortgages: These mortgages have a fixed interest rate for the entire loan term, typically 15 or 30 years. This predictability makes them popular for borrowers who prefer stable monthly payments.
- Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs): ARMs have an interest rate that fluctuates based on a benchmark index, such as the LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate). They often offer lower initial interest rates than fixed-rate mortgages, but the rate can increase over time.
- Interest-Only Mortgages: These mortgages require borrowers to pay only the interest on the loan for a set period, with the principal balance remaining unchanged. This option can be beneficial for borrowers with a short-term need for financing, but it results in higher overall interest costs.
Home Equity Loans
Home equity loans, also known as second mortgages, are secured loans that use the equity in your home as collateral. Equity refers to the difference between the current market value of your home and the outstanding mortgage balance.- Fixed Interest Rates: Home equity loans typically have fixed interest rates, providing borrowers with predictable monthly payments.
- Lump Sum Disbursement: The loan proceeds are received as a lump sum, allowing borrowers to use the funds for various purposes, such as home improvements, debt consolidation, or medical expenses.
- Eligibility Requirements: Borrowers must have sufficient equity in their homes to qualify for a home equity loan. The lender will assess factors like credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio.
Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs)
HELOCs are revolving lines of credit secured by the equity in your home. They provide borrowers with a flexible borrowing option, allowing them to withdraw funds as needed up to a pre-approved credit limit.- Variable Interest Rates: HELOCs typically have variable interest rates, which can fluctuate based on market conditions. This can lead to unpredictable monthly payments.
- Draw Period and Repayment Period: HELOCs have a draw period during which borrowers can access funds, followed by a repayment period where they make regular payments on the outstanding balance.
- Tax Deductibility: Interest paid on home equity loans and HELOCs may be tax-deductible under certain circumstances, but it's essential to consult with a tax advisor to determine eligibility.
How Homeowner Loan Calculators Work: Home Owners Loan Calculator
Homeowner loan calculators are valuable tools that simplify the process of understanding and comparing loan options. They provide quick estimates of monthly payments, total interest paid, and other important financial details, helping you make informed decisions about your mortgage.The Basic Principles of Loan Calculations
Loan calculators work by applying fundamental financial formulas to calculate the various components of a loan. These calculations involve the interplay of three key variables: the loan amount, the interest rate, and the loan term. The calculation of interest is crucial in determining the total cost of a loan. Interest is the price paid for borrowing money, and it's typically expressed as an annual percentage rate (APR). The interest calculation is based on the following formula:Interest = Principal x Interest Rate x TimeWhere: * Principal is the amount of money borrowed. * Interest Rate is the annual percentage rate charged on the loan. * Time is the duration of the loan, typically expressed in years. The principal is the initial amount borrowed, while the monthly payment is the fixed amount paid regularly to repay the loan. The monthly payment comprises both principal and interest, ensuring that the loan is gradually repaid over time.
Loan Calculator Variables
Loan calculators allow you to adjust various variables to see how they impact the loan's overall cost. These variables include: * Loan Amount: The amount of money you want to borrow. This is usually the purchase price of the property minus any down payment. * Interest Rate: The annual percentage rate charged on the loan. Interest rates fluctuate based on market conditions and the borrower's creditworthiness. * Loan Term: The duration of the loan, typically expressed in years. Common loan terms include 15, 20, and 30 years.Impact of Variables on Loan Cost, Home owners loan calculator
Adjusting the loan calculator variables can significantly impact the total cost of the loan. For instance: * Higher Loan Amount: A larger loan amount will result in higher monthly payments and a higher total interest paid. * Higher Interest Rate: A higher interest rate will also lead to higher monthly payments and a greater total interest paid over the loan term. * Longer Loan Term: A longer loan term will result in lower monthly payments but a higher total interest paid over the loan's lifetime. By adjusting these variables, you can explore different loan scenarios and identify the most suitable option based on your financial situation and goals.Using a Homeowner Loan Calculator
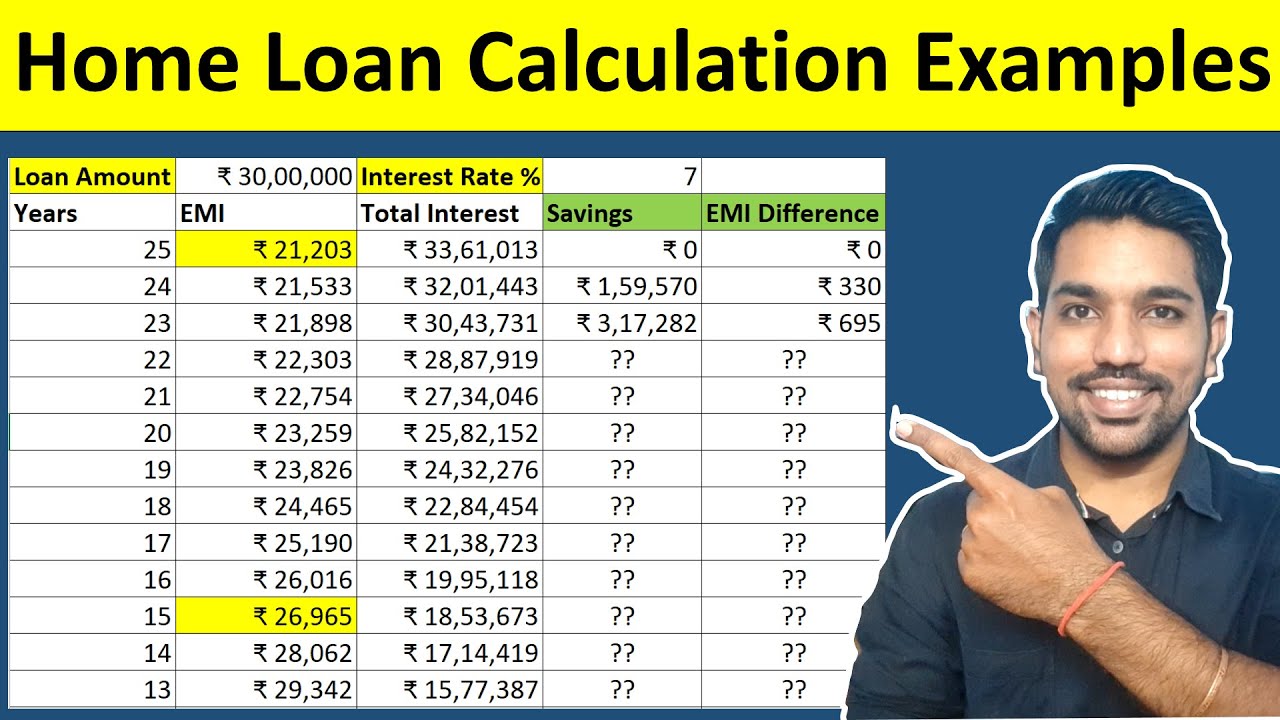 Homeowner loan calculators are valuable tools for understanding the financial implications of a mortgage. They allow you to explore different loan scenarios and determine the best option for your individual circumstances. By inputting specific loan parameters, you can receive instant estimates of your monthly payments, total interest paid, and overall loan cost.
Homeowner loan calculators are valuable tools for understanding the financial implications of a mortgage. They allow you to explore different loan scenarios and determine the best option for your individual circumstances. By inputting specific loan parameters, you can receive instant estimates of your monthly payments, total interest paid, and overall loan cost.
Using a Homeowner Loan Calculator
To use a homeowner loan calculator effectively, follow these steps:- Identify the Loan Parameters: Begin by gathering the essential information needed for the calculator. This typically includes the loan amount, interest rate, loan term, and any additional fees or closing costs.
- Input the Information: Enter the loan parameters into the calculator's designated fields. Most calculators have user-friendly interfaces with clear instructions.
- Review the Results: The calculator will display the estimated monthly payments, total interest paid, and other relevant financial details. Take some time to carefully analyze the results and consider their implications for your budget and financial goals.
Interpreting the Results
Understanding the output of a homeowner loan calculator is crucial for making informed decisions. Here's how to interpret the results:- Monthly Payments: This figure represents the amount you will need to pay each month to repay the loan. It includes both principal and interest payments.
- Total Interest Paid: This figure reflects the total amount of interest you will pay over the life of the loan. It's essential to consider this cost as it can significantly impact the overall loan expense.
- Loan Term: The loan term refers to the duration of the loan, typically expressed in years. A longer loan term generally results in lower monthly payments but higher total interest paid.
Comparing Loan Options
Homeowner loan calculators are particularly useful for comparing different loan options. By inputting various loan parameters, you can assess the financial implications of each option and identify the most suitable choice for your needs.- Interest Rates: Compare the estimated monthly payments and total interest paid for different interest rates. Even a small difference in interest rates can have a significant impact on the overall loan cost over time.
- Loan Terms: Explore the impact of different loan terms on your monthly payments and total interest paid. Consider your financial situation and goals when choosing a loan term.
- Down Payment: Determine how varying down payment amounts affect your monthly payments, total interest paid, and overall loan cost.
Exploring Different Scenarios
Homeowner loan calculators enable you to explore different loan scenarios and analyze their potential outcomes. This allows you to make informed decisions based on your unique circumstances.- Variable vs. Fixed Rates: Compare the potential risks and rewards of variable-rate loans with the stability of fixed-rate loans.
- Loan Programs: Evaluate different loan programs, such as FHA, VA, or conventional loans, to identify the program that best aligns with your financial situation and eligibility criteria.
- Prepayment Options: Explore the impact of making extra payments or prepaying the loan on your overall loan cost and repayment schedule.
Benefits of Using a Homeowner Loan Calculator
 home owners loan calculator" title="Loan calculator homeowner excel" />
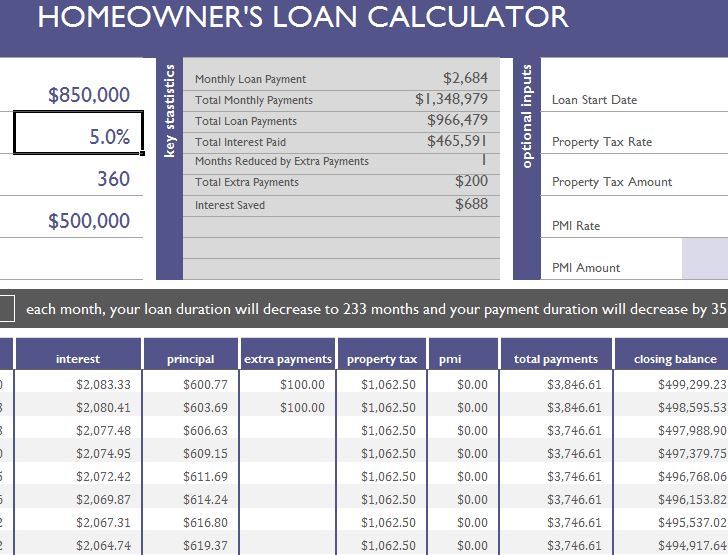
A homeowner loan calculator is a valuable tool that can save you time and money by helping you make informed decisions about your financing options. It can help you compare different loan terms, understand the impact of interest rates, and determine how much you can afford to borrow.
home owners loan calculator" title="Loan calculator homeowner excel" />
A homeowner loan calculator is a valuable tool that can save you time and money by helping you make informed decisions about your financing options. It can help you compare different loan terms, understand the impact of interest rates, and determine how much you can afford to borrow.
Saving Time and Money
A homeowner loan calculator can save you significant time and money by streamlining the loan research process. Instead of manually calculating loan payments, interest, and other costs, a calculator can provide you with instant results, allowing you to quickly compare different loan options and identify the most suitable one for your needs. By quickly identifying the best loan terms, you can avoid wasting time and money on researching less favorable options.Making Informed Decisions
A homeowner loan calculator empowers you to make informed decisions about your financing options by providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the loan terms and costs. It allows you to explore different scenarios, such as varying the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term, to see how these changes affect your monthly payments, total interest paid, and overall cost of the loan. This information helps you make a well-informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and capabilities.Understanding Loan Terms
A homeowner loan calculator helps you understand the key terms of a loan, such as the principal, interest rate, loan term, and monthly payment. It can also calculate the total interest you will pay over the life of the loan, helping you understand the true cost of borrowing. By understanding these terms, you can make more informed decisions about your loan options and choose a loan that fits your financial situation.Identifying Potential Pitfalls
While homeowner loan calculators are powerful tools, it's important to be aware of potential pitfalls to avoid misinterpretations or inaccurate results. It is essential to remember that loan calculators are based on estimates and assumptions. They may not reflect all the costs associated with a loan, such as closing costs, property taxes, or insurance premiums.Always verify the information provided by the calculator with your lender to ensure accuracy and avoid any surprises during the loan process.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Loan
While the interest rate is a crucial factor in determining the cost of a loan, it's not the only aspect to consider. Understanding the full picture, including additional fees and terms, is essential for making a well-informed decision.Loan Fees
Loan fees, often referred to as origination fees, are charges levied by lenders for processing your loan application. These fees are typically a percentage of the loan amount, and they can significantly impact the overall cost of your loan.For instance, a 1% origination fee on a $200,000 loan would amount to $2,000, which is added to the total loan amount.Understanding these fees upfront allows you to accurately calculate the true cost of the loan and compare different loan options.
Closing Costs
Closing costs encompass various expenses incurred during the final stages of the loan process, including appraisal fees, title insurance, and recording fees. These costs can vary significantly depending on the property's location and the lender's requirements.On average, closing costs can range from 2% to 5% of the loan amount, potentially adding thousands of dollars to the overall cost.It's crucial to factor in these costs when budgeting for your loan and to negotiate with the lender to minimize them where possible.
Prepayment Penalties
Prepayment penalties are fees charged by lenders if you repay your loan early. While not all loans include this provision, it's essential to check the loan agreement carefully to avoid unexpected charges.These penalties are often a percentage of the outstanding loan balance, and they can significantly impact your savings if you choose to pay off the loan early.If you anticipate making early payments, consider choosing a loan without prepayment penalties or opting for a loan with a lower penalty rate.
Finding a Reputable Lender
Securing a home loan from a reliable lender is crucial for a smooth and successful home buying experience. A reputable lender will offer competitive rates, transparent terms, and excellent customer service, ensuring a positive and stress-free process.Evaluating Lender Reputation
It is essential to thoroughly research and evaluate potential lenders to ensure you choose a reputable and trustworthy partner for your home loan.- Check Online Reviews and Ratings: Websites like the Better Business Bureau (BBB) and Trustpilot provide valuable insights into a lender's reputation based on customer experiences. Look for lenders with consistently positive reviews and high ratings.
- Verify Licensing and Certifications: Ensure the lender is licensed and certified to operate in your state. You can check with your state's financial regulatory agency to verify their credentials.
- Read Industry Publications and Reports: Reputable financial publications often publish rankings and reviews of mortgage lenders. Consulting these sources can provide additional insights into a lender's performance and reputation.
Comparing Interest Rates and Fees
Understanding the interest rates and fees associated with different loan options is crucial for making informed decisions.- Obtain Multiple Loan Quotes: Contact several lenders to obtain quotes for different loan products. Compare interest rates, loan terms, and associated fees to find the most favorable offer.
- Analyze Loan Terms and Conditions: Carefully review the loan terms and conditions, including the interest rate, loan duration, origination fees, and any other associated charges. Pay attention to prepayment penalties, which can restrict your ability to pay off the loan early.
- Consider APR (Annual Percentage Rate): The APR reflects the total cost of borrowing, including interest rates and fees. Comparing APRs across different lenders can provide a more accurate picture of the overall loan cost.
Understanding Loan Terms
Understanding the different loan terms and their implications is essential for making an informed decision.- Fixed-Rate vs. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages: Fixed-rate mortgages offer a predictable monthly payment for the entire loan term, while adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs) have an initial fixed rate that can adjust over time. Consider your financial situation and risk tolerance when deciding between fixed and adjustable rates.
- Loan Duration: The loan duration, typically expressed in years, influences the monthly payment amount and the total interest paid over the life of the loan. Shorter loan durations result in higher monthly payments but lower overall interest costs.
- Loan Type: There are various types of home loans, such as conventional loans, FHA loans, VA loans, and USDA loans, each with its own eligibility requirements and terms. Consider your specific needs and financial situation when choosing a loan type.
Getting Pre-Approved for a Loan
Getting pre-approved for a mortgage before starting your home search is highly recommended.- Demonstrates Financial Readiness: Pre-approval shows sellers that you are a serious buyer with the financial capacity to purchase a home.
- Establishes a Budget: The pre-approval process provides an estimate of your borrowing capacity, helping you establish a realistic budget for your home purchase.
- Streamlines the Closing Process: Having a pre-approval in place simplifies the closing process, as the lender has already reviewed your financial information and determined your eligibility for a loan.
